TB Test Options
TB Testing: IGRA Blood Test
TB Testing: IGRA Blood Test
TB Testing: IGRA Blood Test

A blood test that measures how your immune system reacts to TB bacteria. The test detects and measures an immune response.
The two main IGRA tests are QuantiFERON Gold
and T-SPOT.
- Single blood draw
- No return visit needed
- Results in 3-4 days
- More convenient for people who can't return for reading
TB Testing: Skin Test
TB Testing: IGRA Blood Test
TB Testing: IGRA Blood Test
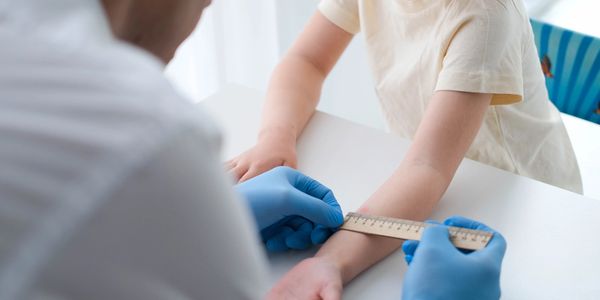
TB (Tuberculosis) testing screens for tuberculosis infection using a skin test to detect immune response to TB bacteria.
- Takes seconds to administer
- Small bump forms under skin
- Return in 48-72 hours for reading
- Healthcare provider measures any reaction
- Positive test requires follow-up (doesn't mean active TB)
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.